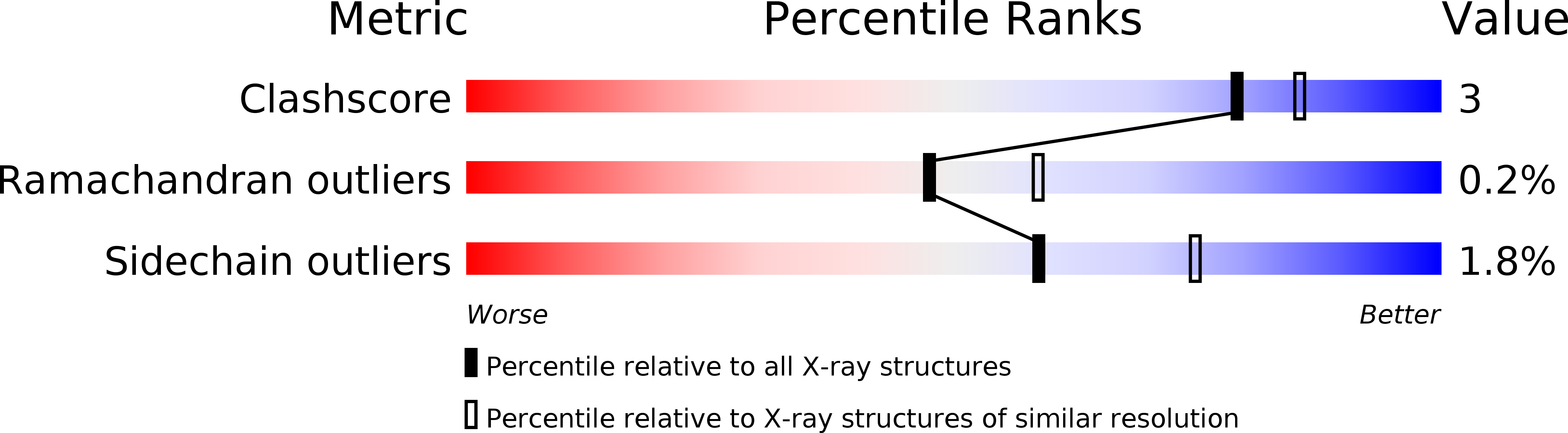
Deposition Date
1994-05-13
Release Date
1994-09-30
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1AGM
Keywords:
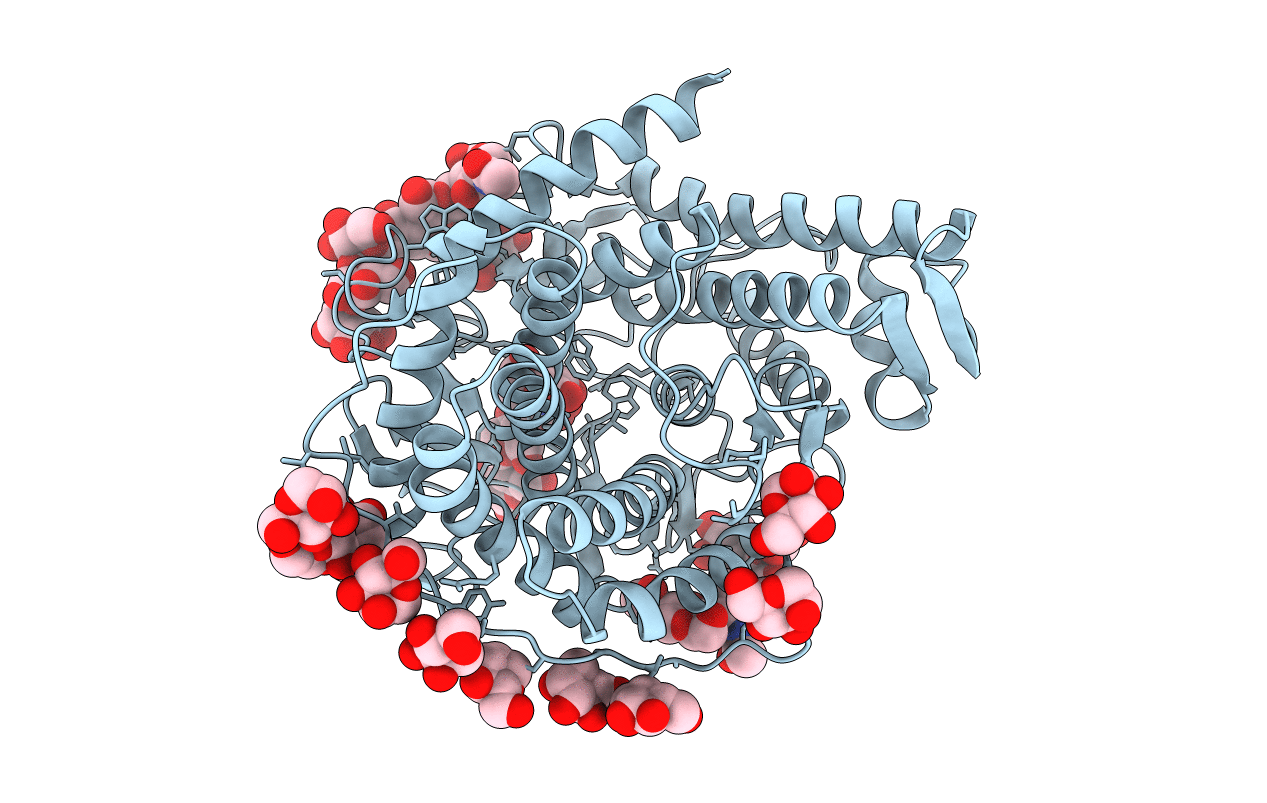
Title:
Refined structure for the complex of acarbose with glucoamylase from Aspergillus awamori var. x100 to 2.4 angstroms resolution
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Aspergillus awamori (Taxon ID: 105351)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.30 Å
R-Value Observed:
0.12
Space Group:
P 21 21 21