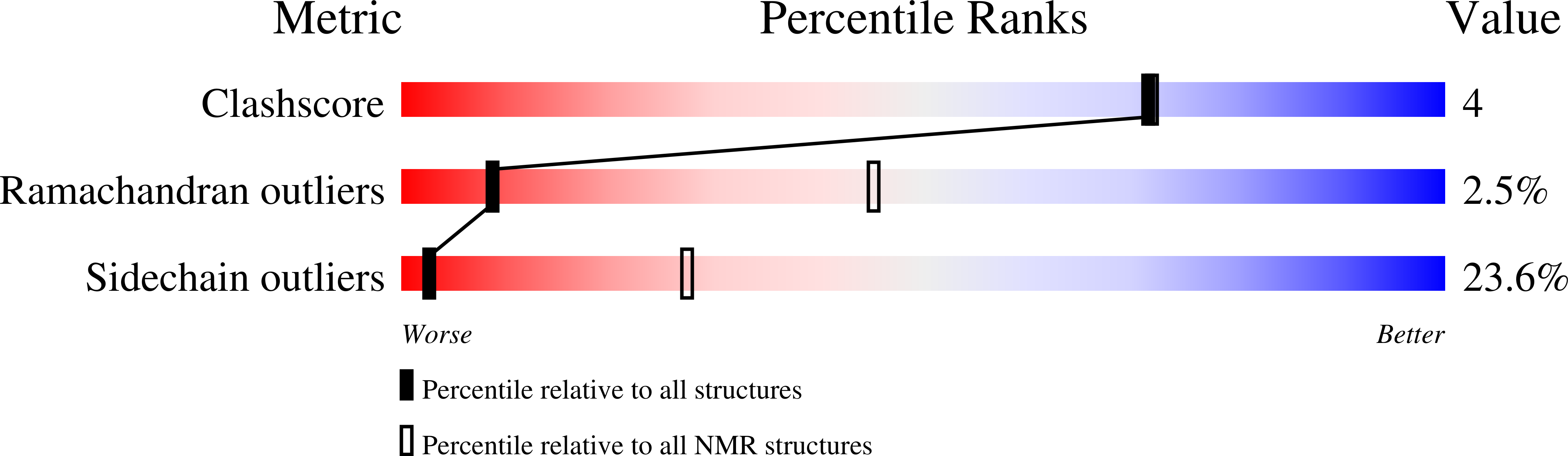
Deposition Date
1997-04-03
Release Date
1998-04-08
Last Version Date
2022-02-16
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
50
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
LOWEST ENERGIES AND LEAST NUMBER OF RESTRAINT VIOLATIONS