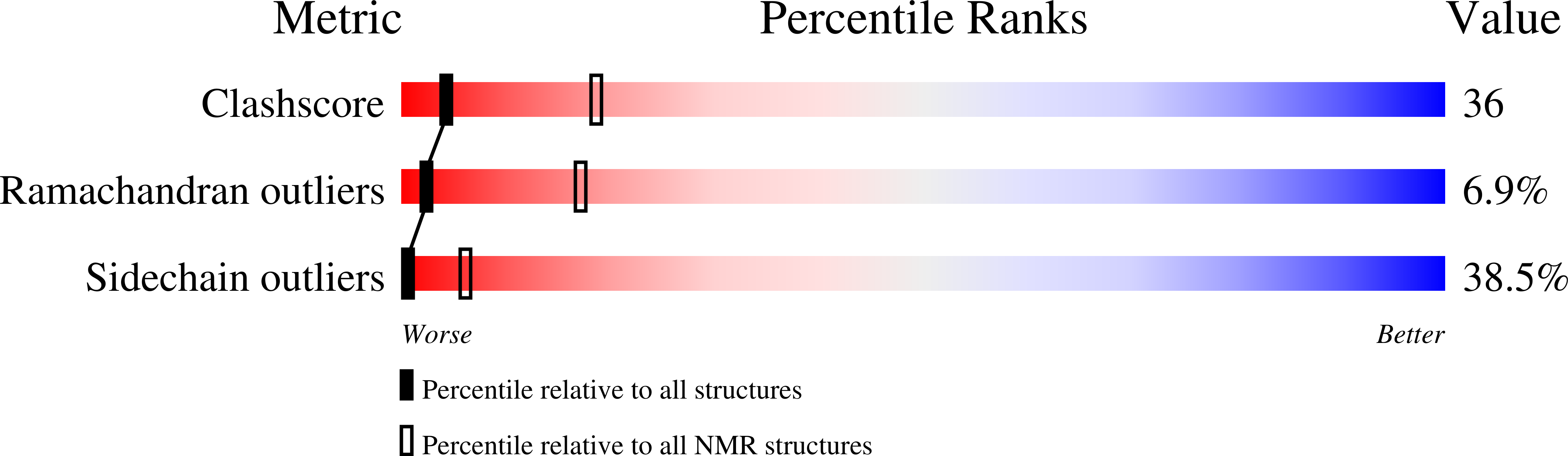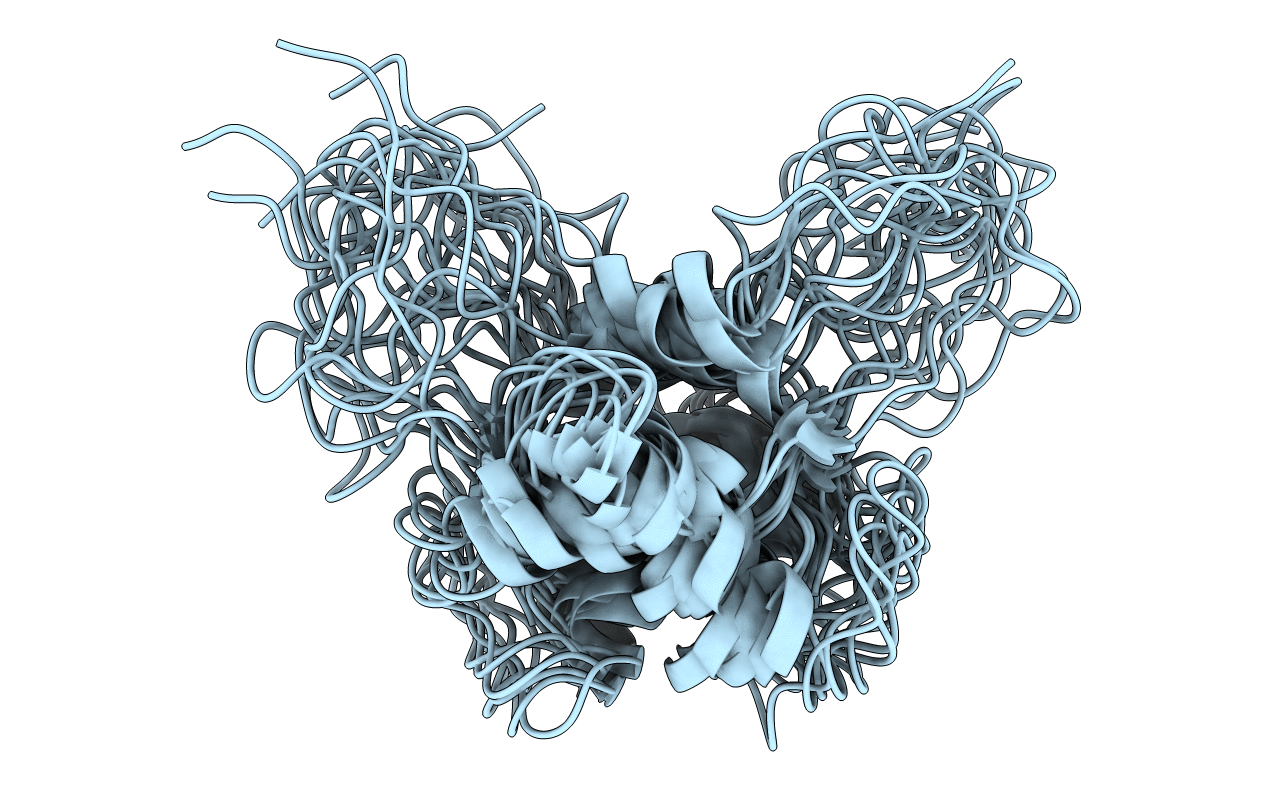
Deposition Date
1997-02-07
Release Date
1998-01-14
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1ACI
Keywords:
Title:
L11 RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN RNA BINDING DOMAIN, NMR, 20 STRUCTURES
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Geobacillus stearothermophilus (Taxon ID: 1422)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
50
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
MINIMUM ENERGY AND LEAST RESTRAINT VIOLATION