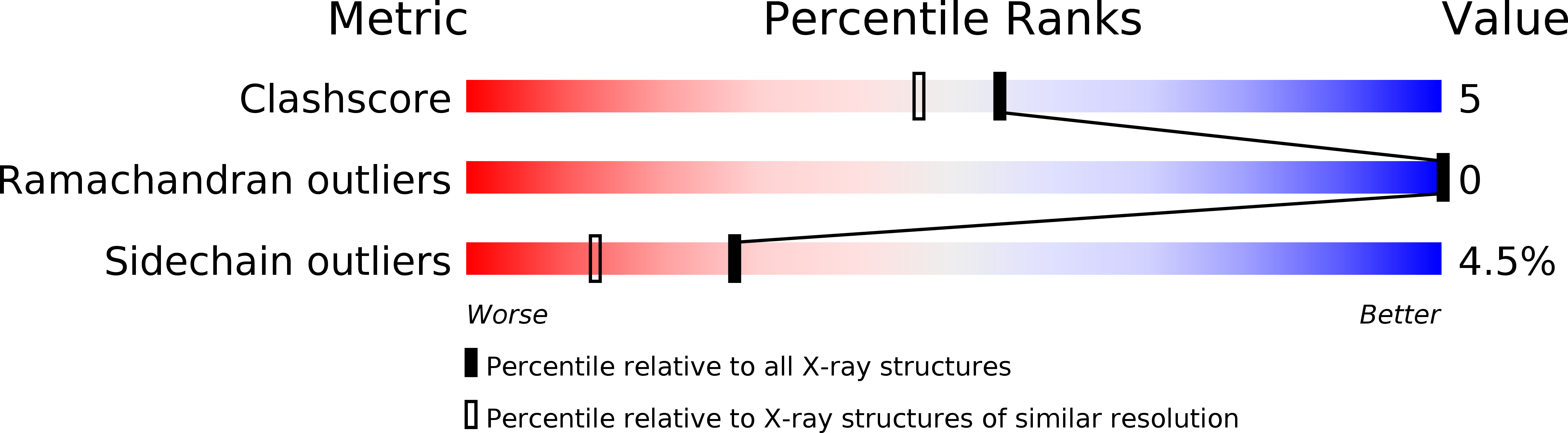Deposition Date
1998-03-31
Release Date
1999-05-11
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1A82
Keywords:
Title:
DETHIOBIOTIN SYNTHETASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI, COMPLEX WITH SUBSTRATES ATP AND DIAMINOPELARGONIC ACID
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.80 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.19
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
C 1 2 1