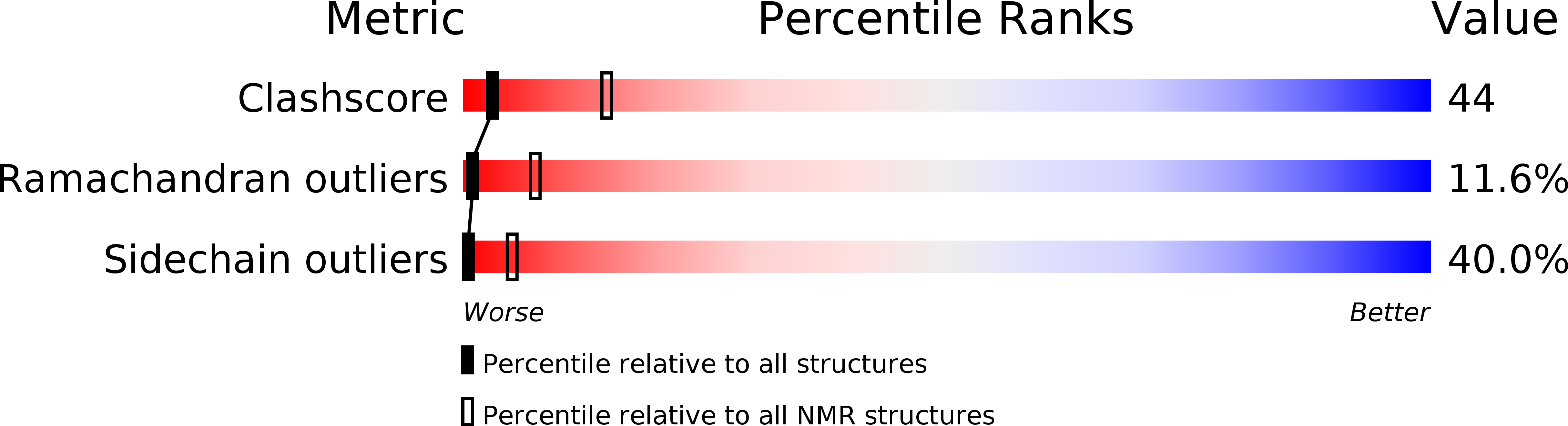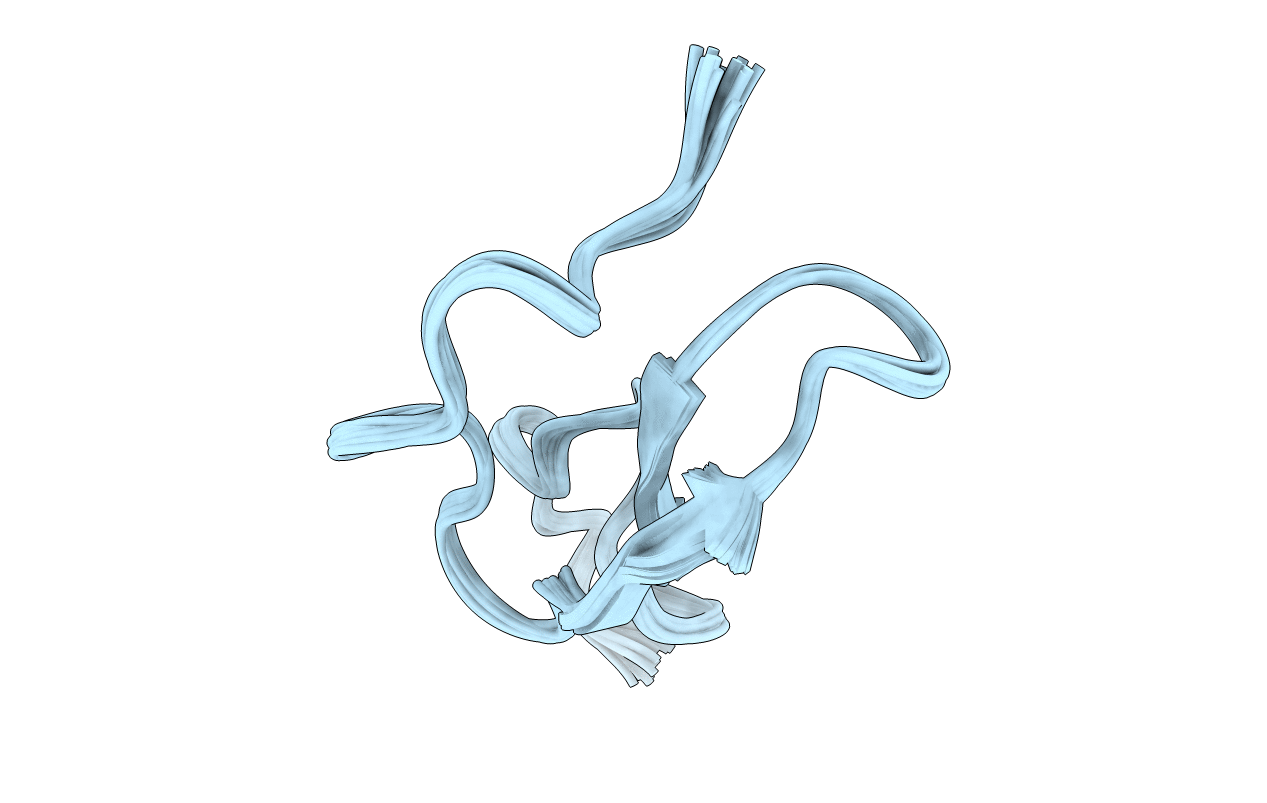
Deposition Date
1998-01-22
Release Date
1998-07-29
Last Version Date
2025-03-26
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1A3P
Keywords:
Title:
ROLE OF THE 6-20 DISULFIDE BRIDGE IN THE STRUCTURE AND ACTIVITY OF EPIDERMAL GROWTH FACTOR, NMR, 20 STRUCTURES
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
1000
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
20 BEST, BASED ON STEREOCHEMICAL AND NOE ENERGIES