Deposition Date
1997-12-10
Release Date
1998-04-08
Last Version Date
2023-08-02
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
1A1B
Keywords:
Title:
C-SRC (SH2 DOMAIN) COMPLEXED WITH ACE-PHOSPHOTYR-GLU-(N,N-DIPENTYL AMINE)
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
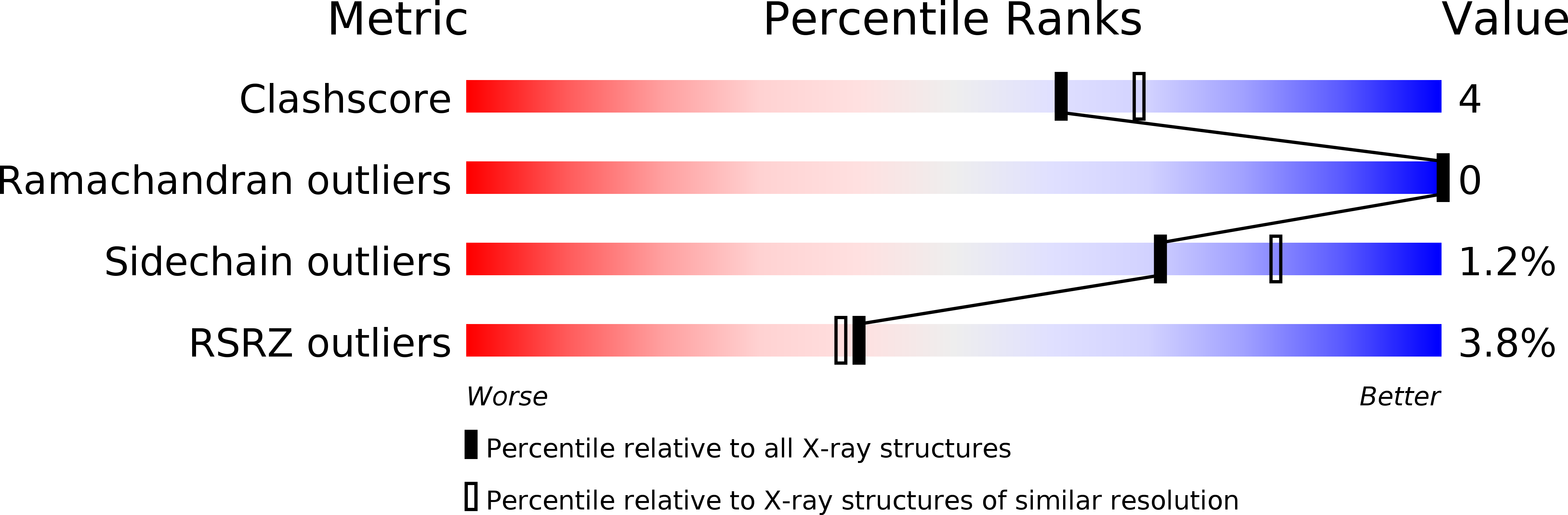
Resolution:
2.20 Å
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.17
Space Group:
P 21 21 21