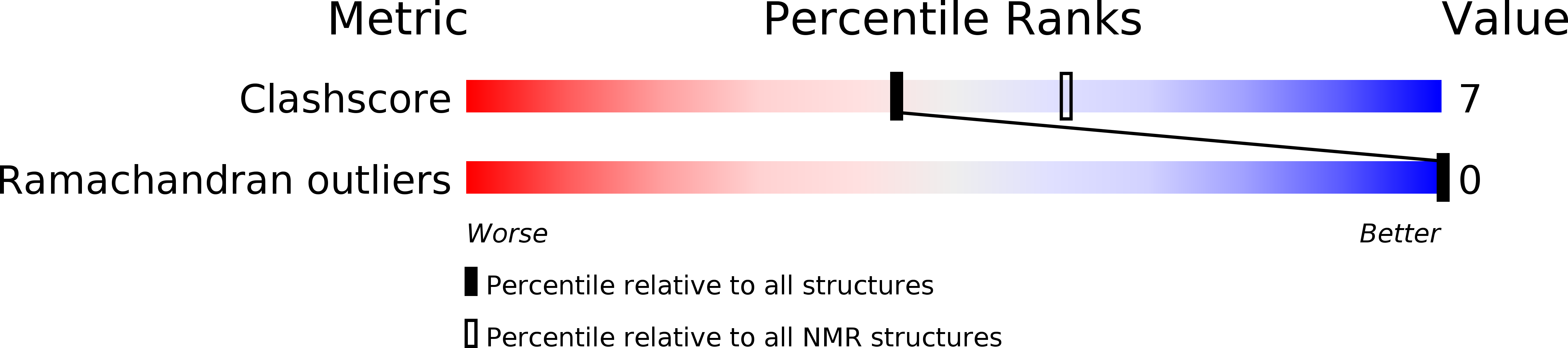
Deposition Date
1994-09-30
Release Date
1995-02-27
Last Version Date
2025-03-26
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
193D
Keywords:
Title:
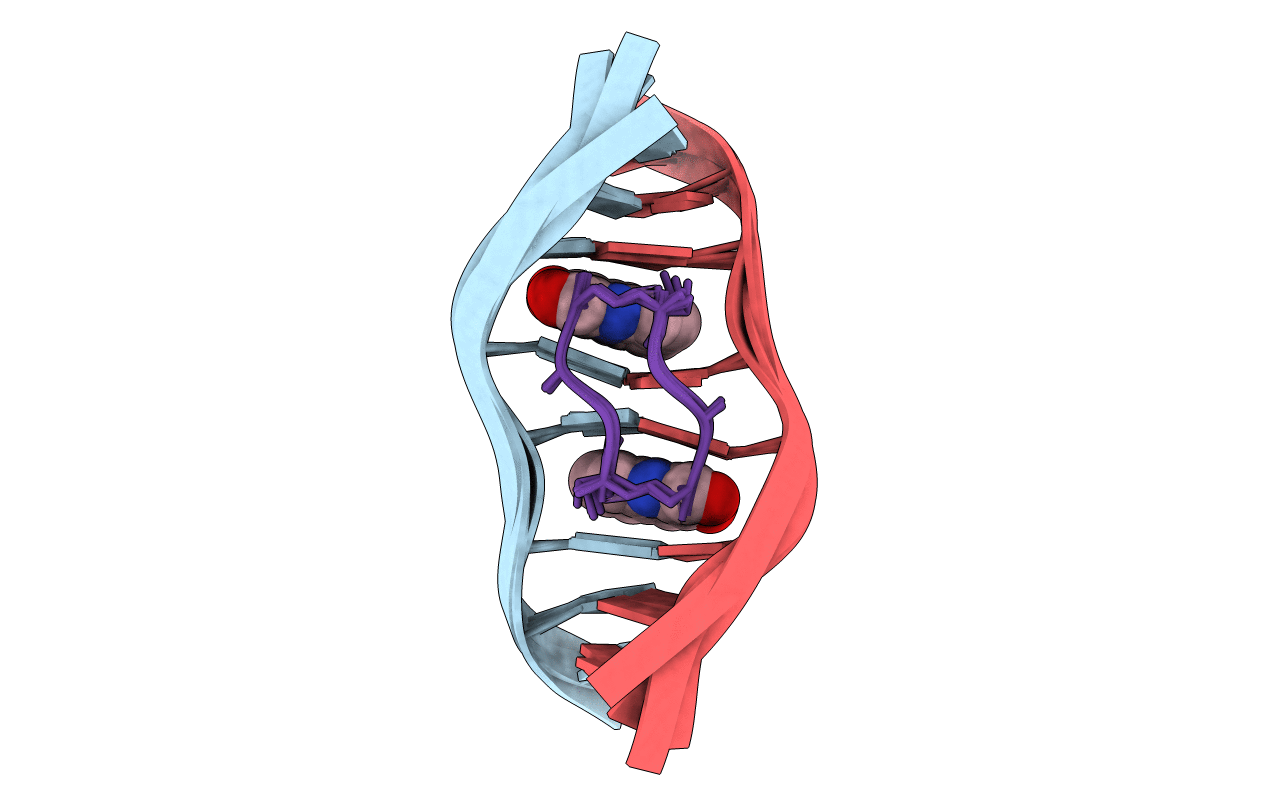
SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF A QUINOMYCIN BISINTERCALATOR-DNA COMPLEX
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
4
Conformers Submitted:
4
Selection Criteria:
all calculated structures submitted