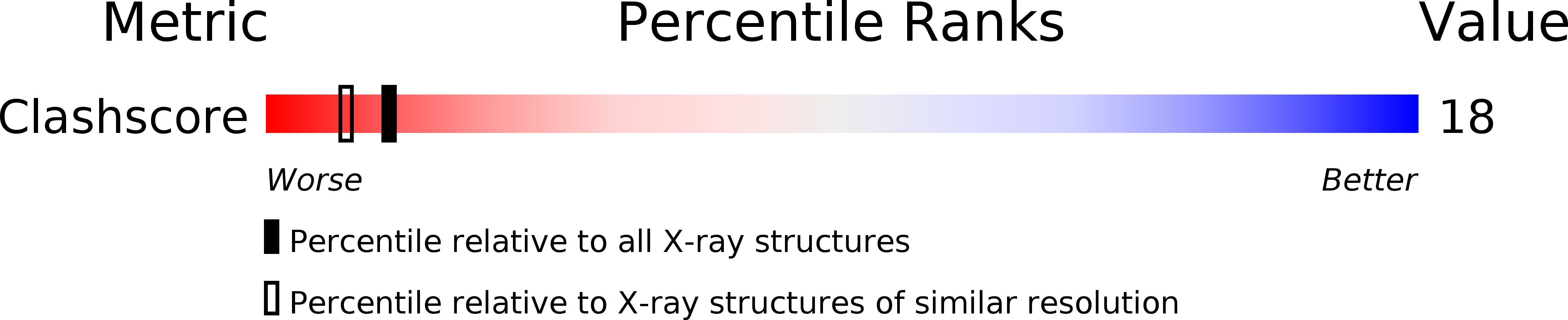
Deposition Date
1993-01-04
Release Date
1993-07-15
Last Version Date
2024-02-07
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
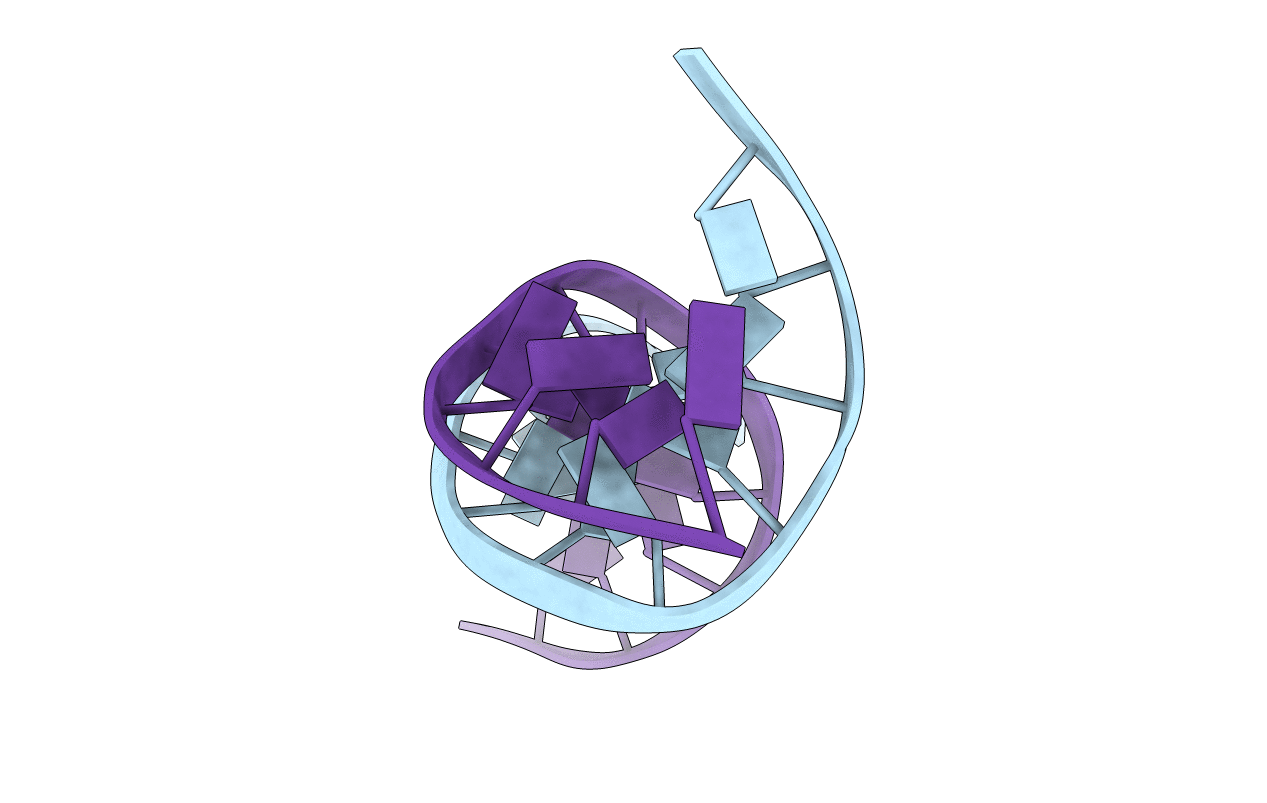
111D
Keywords:
Title:
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE AND STABILITY OF A DNA DUPLEX CONTAINING A(ANTI).G(SYN) BASE-PAIRS
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.25 Å
R-Value Observed:
0.16
Space Group:
P 21 21 21